Is your website not appearing at the top of search results? Do you feel like your traffic is decreasing and conversions aren’t meeting expectations? In today’s blog, we’ll discuss the basic SEO audit steps that can improve your website’s ranking, attract more visitors, and strengthen your online presence! If you want to see your website at the top of search engines, this blog is for you. Let’s get started!
First, we’ll explain what an SEO audit is and why it’s important. Then, we’ll go step-by-step through the key areas you need to focus on—from site speed to backlinks, technical issues to content quality—we’ll cover everything! You’ll also get practical tips that you can immediately apply to your website. So, if you want to take your site’s performance to the next level, make sure to read this blog till the end!
And yes, if you want to learn more helpful tips and tricks to grow your website, don’t forget to subscribe to our blog! You’ll find regular content on SEO, digital marketing, and much more to help your online business grow.
Step 1: Check for Indexing Issues
First, let’s talk about the first step in an SEO audit—checking for indexing issues. If your pages aren’t indexed in Google’s database, they won’t rank in search results, so this step is very important.
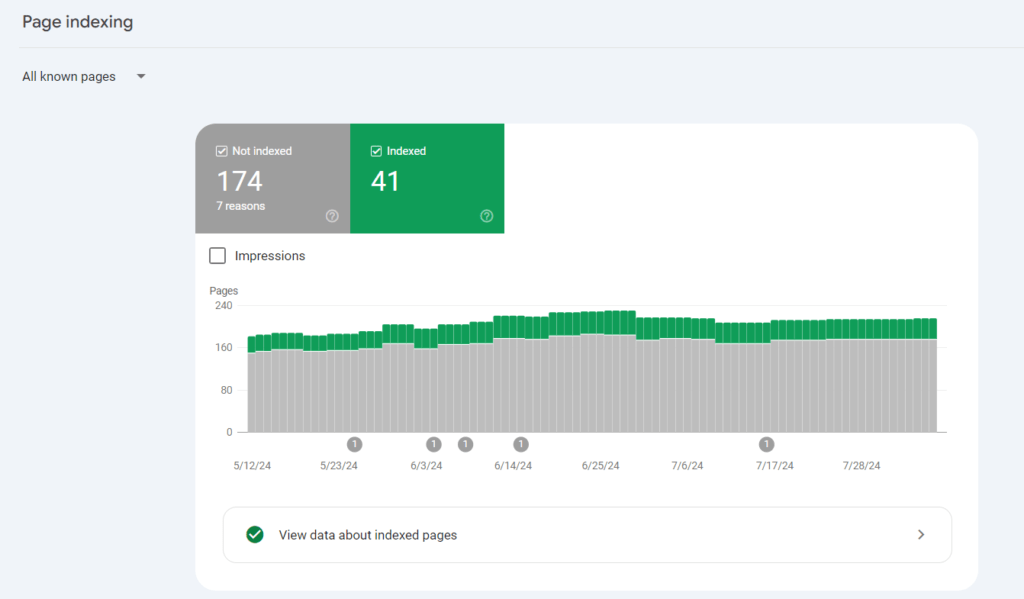
You can check the status of your pages in Google Search Console under the ‘Pages’ report in the ‘Index’ section. This report shows which pages are indexed and which are not, along with the reasons why some pages may not be indexed.
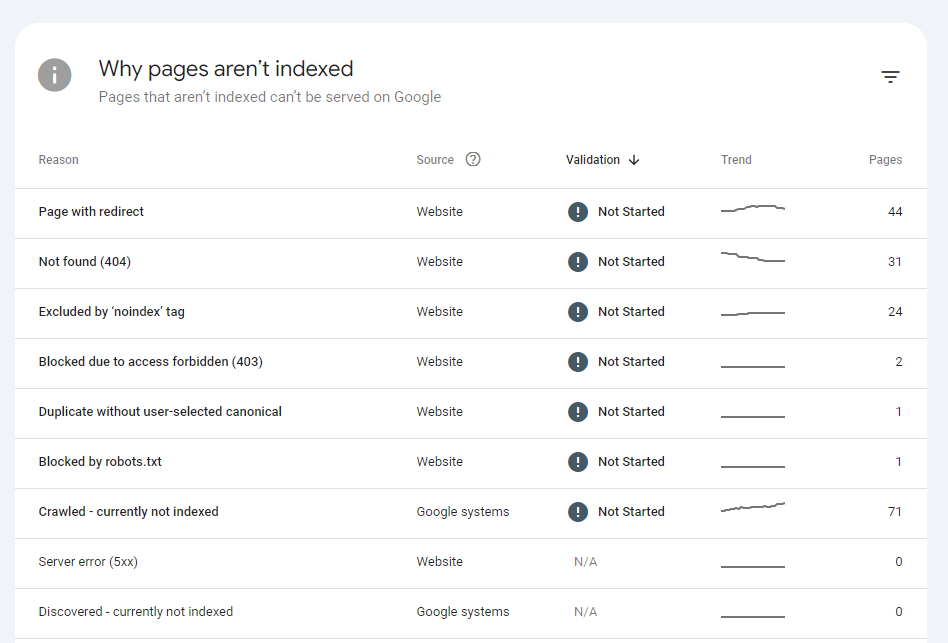
Remember, not every page needs to be indexed—only the ones you want to rank in search results. Some URLs like redirects, admin pages, or pages with canonical tags don’t need to be indexed.
If you find a page that should be indexed but isn’t, follow Google’s guidelines to fix the issue. After fixing it, click the ‘Validate Fix’ button to inform Google that the issue is resolved. You can also request Google to index a URL by clicking the ‘Request Indexing’ link.
Step 2: Check for Duplicate Versions of Your Site
Checking for duplicate versions of your site. It’s important to make sure Google is indexing only one version of your site. Your site can run on multiple versions, like:
For search engines, these are all different versions, and if they’re all active, it can cause issues with crawling, indexing, and ranking. This can also slow down your PageRank, negatively affecting your SEO rankings.
Checking this is simple. Just type each version of your site into a web browser. Ideally, you should be automatically redirected to your preferred version. For example, if your preferred URL is https://yoursite.com, entering any other version should redirect you there.
If your site is live on multiple versions, you’ll need to set up proper redirects in your web server or CMS settings. This step will ensure that Google treats your site as a single entity.
Step 3: Check for Manual Actions
Checking for manual actions. If your site has violated Google’s spam policies, you might receive a manual action, which means your site’s rankings could drop. This manual action can apply to a specific page or the entire site.
Some common reasons for a manual action include:
- Keyword stuffing
- Unnatural links (from or to your site)
- Various kinds of spam
- Thin content with little or no added value
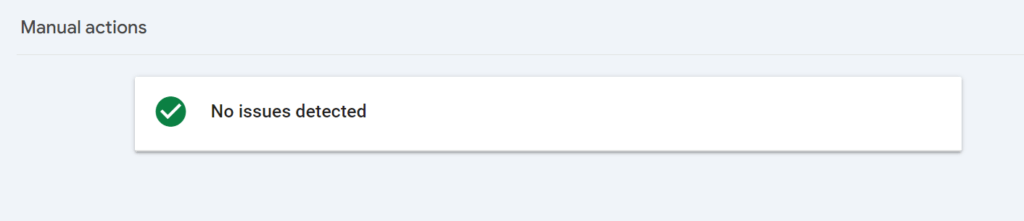
You can check if your site has a manual action by clicking the ‘Manual actions’ link under the ‘Security and Manual Actions’ section in Google Search Console. If you see a green tick, everything is fine!
Step 4: Check for Mobile-Friendliness Issues
Checking for mobile-friendliness issues. In today’s mobile-first world, if your site isn’t mobile-friendly, you’re not considering the user experience. Mobile-friendliness is an important factor in Google’s Page Experience signals and has been a ranking factor since 2015.
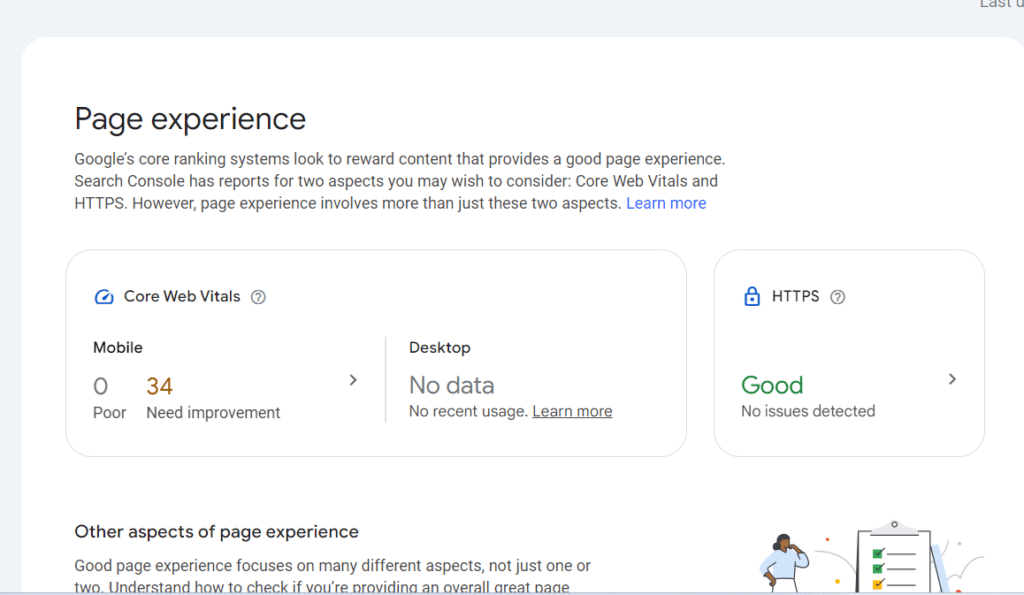
You can check how your site performs on mobile devices by looking at the ‘Mobile Usability’ report in Google Search Console under the ‘Experience’ section. This report will show how your site is performing on mobile devices and any issues that might be present.
Step 5: Analyze Your Site’s Speed
Analyzing your site’s speed. Nowadays, how quickly your site loads is very important. Page speed is a ranking factor, and it also affects user experience. Data shows that if a page loads slowly, users are more likely to leave the website.
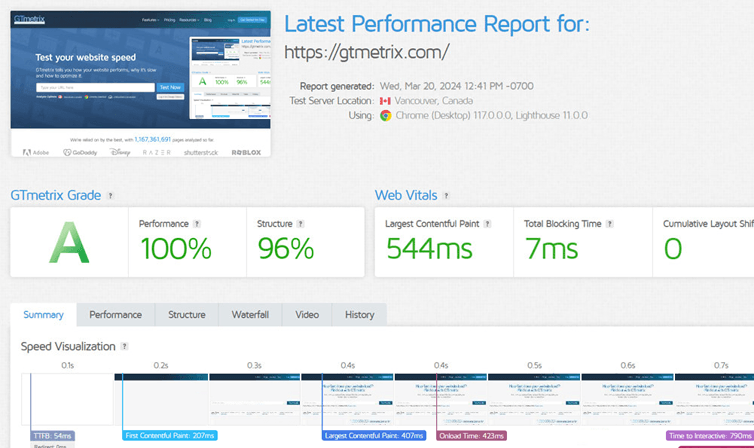
The more issues you fix, the better your site’s speed and rankings will be. So, try to fix as many issues as possible to improve your site’s speed!
Step 6: Analyze Your Core Web Vitals
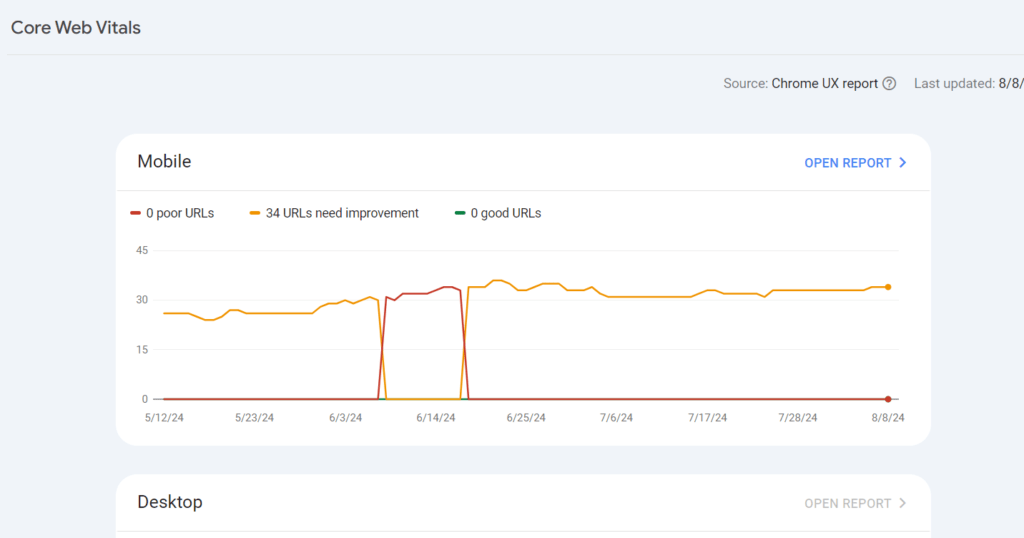
Analyzing your Core Web Vitals. In 2020, Google introduced three new metrics related to page speed and user experience.
It’s important to understand these metrics:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures how long it takes for the largest content on the page to load.
- First Input Delay (FID): Measures the delay between the user’s first interaction and the browser’s response.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Measures how much the layout of the page shifts and how stable the visual experience is.
These metrics can be found in the Core Web Vitals report in Google Search Console. By analyzing these metrics, you can improve your site’s user experience and positively impact your rankings.
Step 7: Analyze Your Internal Links
Internal links are very important for SEO, and there are three main reasons for this:

- Helps Search Engines Crawl: Internal links help search engines reach different pages on your website.
- Helps Users Navigate: These links help users easily reach different sections and important pages of your website.
- Directs Link Equity: Internal links allow you to transfer link equity, or “authority,” to your most important pages.
Step 8: Check Your Organic Traffic
Organic traffic refers to the visitors who come to your website through unpaid, organic search results. This is an important indicator of SEO success.
To check your organic traffic, open the ‘Search results’ report under the ‘Performance’ section in Google Search Console. Here, you’ll find four main metrics.
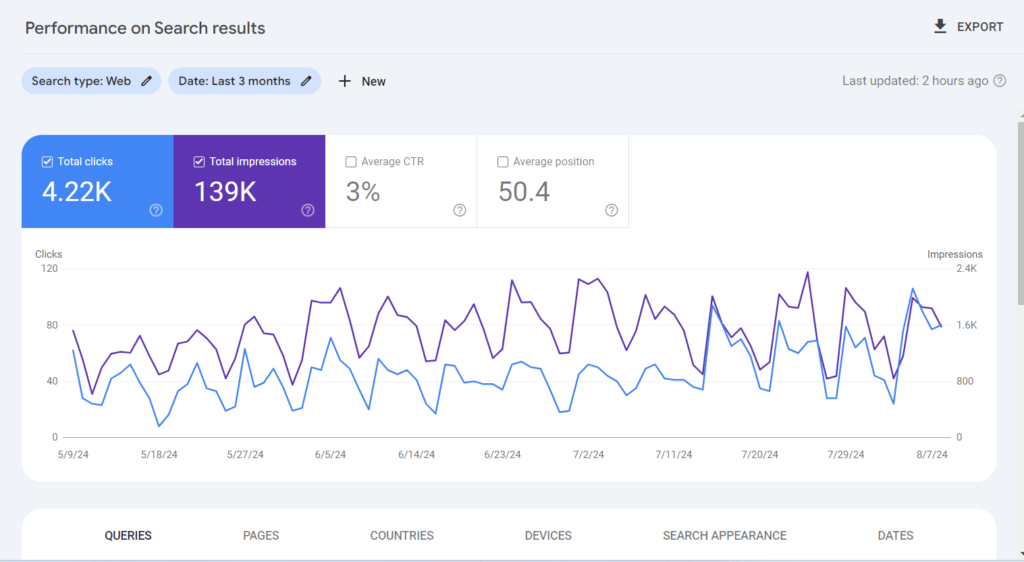
The most interesting metric here is ‘Total clicks,’ which shows how many times users clicked on your site in a specified time frame. You can configure the report by queries, pages, devices, and countries.
These reports will give you detailed information about your organic traffic and help you establish benchmarks and track progress. By reading Google’s Search Performance report guide, you can learn more about this report and its functions.
Step 9 : Ensure Your Sitemap Doesn’t Have Any Issues
A sitemap is a list of the pages on your website that you want search engines to index. However, it’s important to make sure that only the important pages are listed in the sitemap.
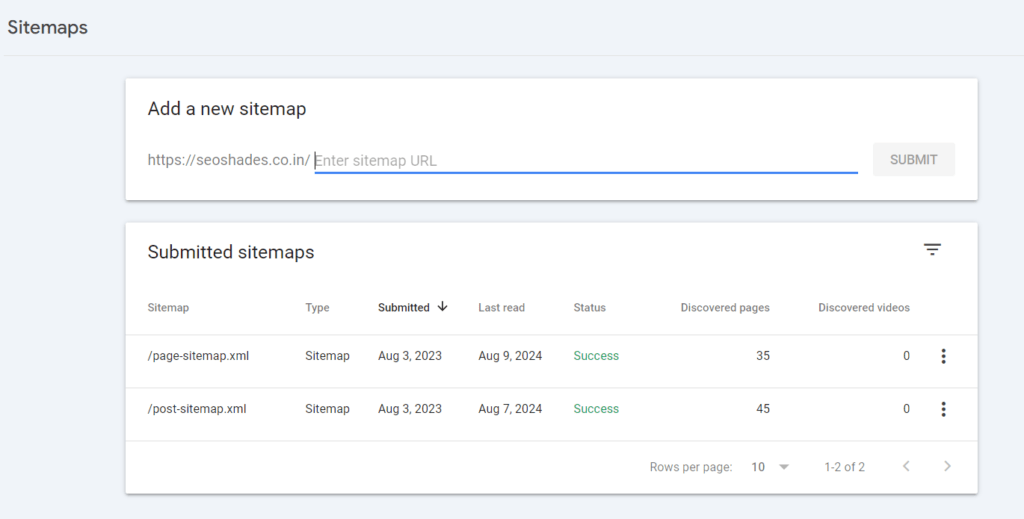
Your sitemap shouldn’t contain redirects, non-canonical pages, or dead pages, as these can send mixed signals to Google. It’s important that your sitemap only includes the pages you want to be indexed. You can monitor your sitemap issues by checking the ‘Sitemaps’ section in Google Search Console.
Step 10: Improve Your On-Page SEO
Improving your on-page SEO. On-page SEO is super important for your website’s overall performance. However, not everyone has the time to optimize all pages immediately.
So, first, identify the 5 most important pages on your site. These pages might be:
- Targeting an important keyword
- Experiencing a decline in traffic recently
- Already ranking but have the potential to reach the top 5
For example, if you have a page already ranking on the first page, it’s essential to optimize it to move into the top 3.
If you’re short on time, focus on these 5 strategies:
- Include your keyword in the title tag
- Add the keyword within the first 100 words
- Add 5+ external links
- Add 5+ internal links (more details in the next step)
- Use helpful, SEO-optimized images
These small improvements can help your important pages reach Google’s top results and boost your site’s overall SEO performance.
Step 11: Remove “Zombie Pages”
Now, let’s move on to the eleventh step—removing “Zombie Pages.” These are pages that don’t add value to your site, don’t drive traffic, and aren’t helpful to users. However, they use up your crawl budget, negatively affecting your site’s overall SEO performance.
First, type site:yourwebsite.com into Google. This will show you how many pages Google has indexed. If this number is higher than expected, it’s likely that you have “Zombie Pages” on your site
Common types of “Zombie Pages” include:
- Irrelevant archive pages
- Empty category or tag pages (especially on WordPress sites)
- Search result pages
- Old press releases
- Thin content
Step 12: Audit Your Backlinks
Auditing your backlinks. Backlinks are one of the most important ranking factors for SEO. A strong backlink profile can significantly improve your site’s search rankings, while low-quality backlinks can do more harm than good.
Start by checking your backlinks in Google Search Console under the ‘Links’ section. Here, you’ll see your top linked pages, referring domains, and anchor text. Pay attention to backlinks that may come from spammy or low-quality sites.
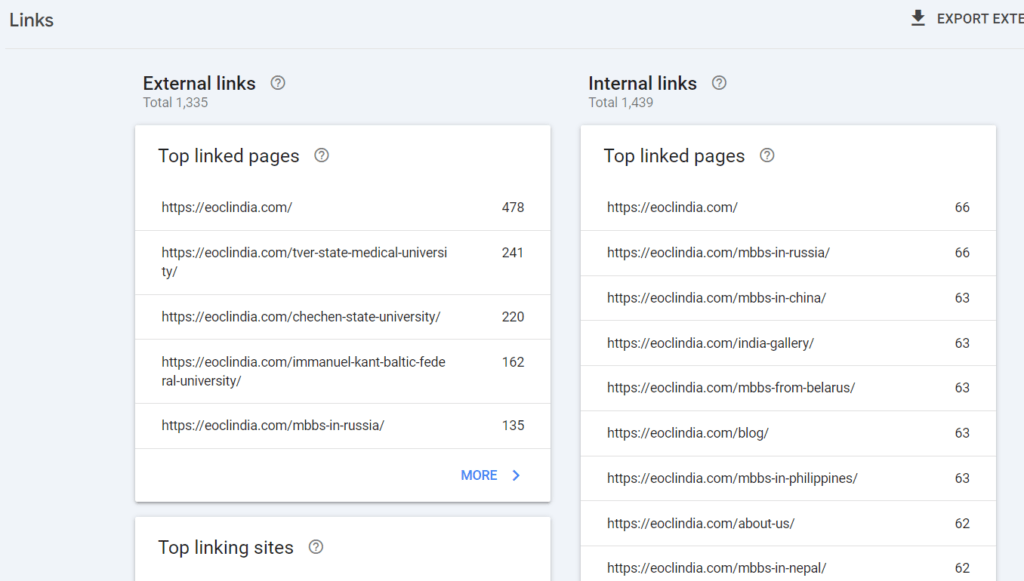
If you identify any harmful backlinks, consider disavowing them using Google’s Disavow Tool. However, use this tool with caution, as it can have serious implications on your site’s rankings.
Also, identify high-authority websites in your niche where you can earn backlinks. This could include guest blogging, outreach, or creating valuable content that others naturally want to link to. A strong backlink profile is vital for improving your site’s domain authority and overall SEO performance.
Step 13: Fix Broken Links
Google mentioned a few years ago that broken links don’t matter much to them, but broken links are not good for user experience, and poor user experience can hurt your SEO.
You can use different tools to fix broken links on your site. One option is to use a free tool like “Broken Link Check,” which will give you a list of broken links on your site. Crawling software like “Screaming Frog” is also a powerful tool that shows you 404 errors and broken links.
Semrush Site Audit is another great way to identify broken links. With these tools, you can fix broken links and improve both the user experience and SEO of your site. So, if your site has broken links, fix them right away. This small action can give a big boost to your site’s overall performance!
Step 14: Audit Your Structured Data
Structured data, also known as schema markup, helps search engines understand your content. It can help you get rich snippets in search results, which boost your site’s visibility in the SERPs.
Rich snippets can improve your CTR (Click-Through Rate). With structured data, you can tell Google about your post’s author, your business information, and much more.
To check if your structured data is implemented correctly, you can use a tool like “Schema Validator.” This tool will tell you if there are any errors in your schema markup and how to fix them.
By auditing your structured data, you can ensure that your markup is implemented correctly, increasing the chances of your site getting rich snippets. This small check can give your SEO efforts a final polish!
In summary, a thorough SEO audit involves analyzing and optimizing various aspects of your website, from technical issues to content quality and backlinks. By following these 14 steps, you can improve your website’s rankings, attract more visitors, and enhance the overall user experience.